Chapter 7 Exercises
Exercise 6: Sorting Arrays:
With PHP there are a variety of ways to sort an array (sort refers to an alphabetical sort if the values being sorted are strings, or a numerical sort if the values being sorted are numbers). When you are sorting an array, you must keep in mind that an array consists of pairs of keys and values. Thus, an array can be sorted based on the keys or the values. This is further complicated by the fact that you can sort the values and keep the corresponding keys aligned, or you can sort the values and have them be assigned new keys.
To sort the values without regard to the keys, you use sort(). To sort these values (again, without regard to the keys) in reverse order, you use rsort(). The syntax for every sorting function is:

So, sort() and rsort() are used as follows:

To sort the values while maintaining the correlation between each value and its key, you use asort(). To sort the values in reverse while maintaining the key correlation, you use arsort().
To sort by the keys while maintaining the correlation between the key and its value, you use ksort(). Conversely, krsort() sorts the keys in reverse. Table 7-2 lists all these functions.
Table 7-2: These functions sort arrays in different ways.
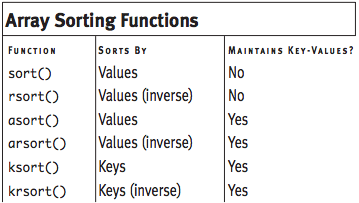
Finally, shuffle() randomly reorganizes the order of an array.
In this exercise you will create a list of students and the grades they receive on a test. You will then sort this list, first by grade and then by name.
To sort an array:
- You will create a PHP script (Script 7-5):
Script 7-5: PHP provides a number of different functions for sorting arrays, including arsort() and ksort() (usedhere).
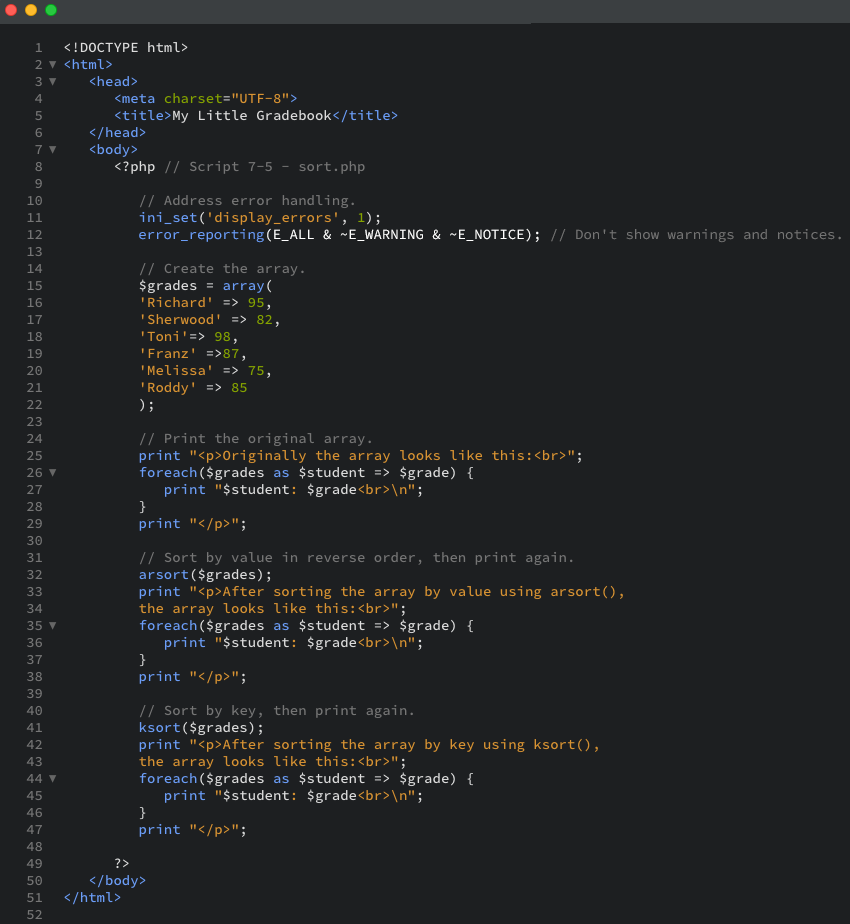
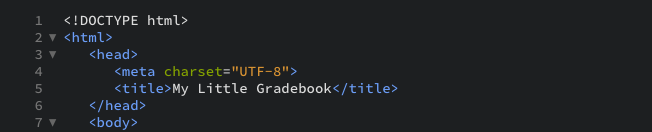
- To begin, create a new HTML document (Script 7-5) with the title My Little Gradebook:
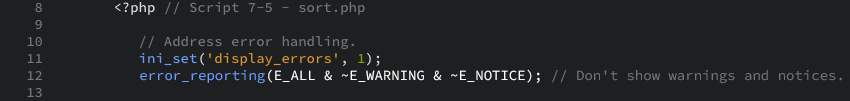
- Begin the PHP section, and address error handling, if necessary:
- Create the array:
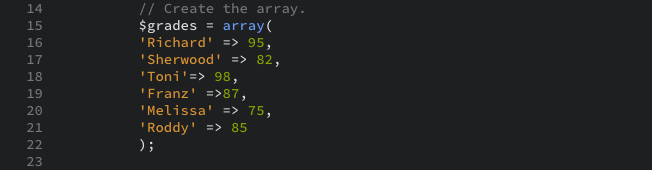
The $grades array consists of six students’ names along with their corresponding grades. Because the grades are number values, they do not need to be quoted when assigning them. - Print a caption, and then print each element of the array using a foreach loop:

The caption tells you what point in the script you are at. At first, it prints the array in the original order. For this you will use a foreach loop, where each index (the student’s name) is assigned to $student, and each value (the student’s grade) is assigned to $grade. The final print() statement closes the HTML paragraph. - Sort the array in reverse order by value to determine who has the highest grade:

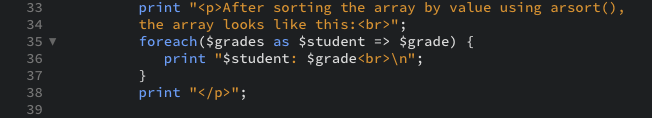
To determine which student has the highest grade, you need to use arsort() instead of asort(). The latter, which sorts the array in numeric order, would order the grades 75, 82, 85, and so on, rather than the desired 98, 95, 87. You must also use arsort() and not rsort() in order to maintain the key-value relationship (rsort() would eliminate the student’s name associated with each grade). - Print the array again (with a caption), using another loop:
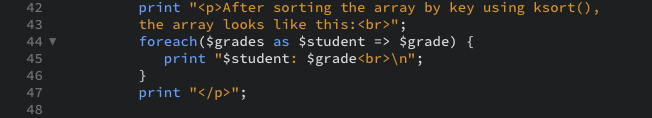
- Sort the array by key to put the array in alphabetical order by student name:

The ksort() function organizes the array by key (in this case, alphabetically) while maintaining the key-value correlation. - Print a caption and the array one last time:
- Close the script with the standard PHP and HTML tags:

- Save the script as sort.php to your XAMPP folder (c:\XAMPP\htdocs\202\chapter7).
- Using Cyberduck, upload the file to the production server, and test in your browser (Figure 7-8), making sure you are looking at the production server version of the file.
Figure 7-8: You can sort an array in a number of ways with varied results. Pay close attention to whether you want to maintain your key-value association when choosing a sort function.


- The $grades array could have been created using the grades as the keys and the names of the students as values. It works either way.
- The natsort() and natcasesort() functions sort a string (while maintaining key-value associations) using natural order. The most obvious example of natural order sorting is that it places name2 before name12, whereas sort() orders them name12 and then name2.
- The usort(), uasort(), and ursort() functions let you sort an array using a user-defined comparison function. These functions are most often used with multidimensional arrays.






